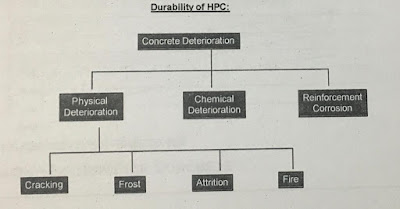
STANDARD PROCTOR COMPACTION TEST
 |
| PROCTOR COMPACTION TEST |
STANDARD PROCTOR COMPACTION TEST
hello, In this post we will be going over The Laboratory procedure is used for a standard Proctor compaction test this Post will demonstrate how to conduct a standard Proctor compaction test in accordance with ASTM (American Society for Testing and materials) specifications.
This test was developed to evaluate the level of compaction on field of compacted soils In the proctor compaction test the soil is compacted into a mould as specific energy ➵➵➟comparable to the energy used in the field the laboratory practice is performed at varying moisture contents to establish a dry density versus moisture content plot.
From this plot the maximum value not weight and optimum moisture content can be determined the practical application of this test in geotechnical engineering is for compacted specification of soils the maximum dry unit weight obtained from this test can be used to determine the relative compaction of soils in the field.
EQUIPMENT’S FOR PROCTOR COMPACTION TEST
The equipment required for the standard Proctor compaction test is➯
➱4-inch mould having
➱volume of one thirtieth of a cubic foot
➱collar,
➱standard Proctor compaction hammer measured weighing five-and-a-half pounds and dropping 12 inches to moisture content cans,
➱steel straight edge,
➱large mixing pan,
➱graduated cylinder capable of holding up to 250 millilitres
➱spray bottle,
➱metal spoon
➱knife we’ll also be needing
➱digital balance
➱oven for moisture content determination
In a sample extractor the soil that we will be performing the standard proctor compaction test on as a low clay silt obtained from the Mississippi River Valley the soil has been mechanically pulverized than air dried the lab documents pertaining to today’s lab can be found on blackboard the handout is posted there and is titled C 215 laboratory number five Proctor compaction testing in addition an ASTM standard pertaining to this lab is also posted ASTM the 46 98 pertains to practicum passion testing also available is today’s datasheet
PROCEDURE OF PROCTOR COMPACTION TEST
The proctor compaction test consists of mixing soil with water to a predetermined moisture content the soil water mixture is then compacted into a mold of a specific volume with a standardized energy at low moisture contents.inter-particle friction will hinder compaction resulting in a low unit weight as moisture increases the friction in between the particle reduces and the particles will compact into a more dense pattern.
 |
| PROCTOR COMPACTION TEST |
At past a certain moisture content notice the optimum moisture content water will start to take the place of dry soil particles and the dry unit weight will again go down by conducting several standard Proctor tests at varying moisture contents.
This curve can be established in the maximum dry unit weight and corresponding moisture content can be determined to perform the proctor compaction test.
Start by weighing the empty Proctor mould without the collar, record the empty weight on your data sheet also weigh the two moisture content cups and record their weights as well, with a caliper record the dimensions of the mould so the volume can be calculated average three equally spaced diameter dimensions in three equally spaced Heights dimensions so that an accurate measurement of volume can be established way out approximately 2,000 grams of the provided air dried soil,
Now that we have our soil weighed out the desired amount of water to add to the soil must be determined the weight of the water that needs to be added to our soil can be determined from this equation,
The weight of the water equals the weight of the soil 2,000 grams in this case times the final moisture content minus the initial moisture content the final moisture content is the target moisture content which I have selected to be 15% the initial moisture content is all the water that is trapped inside the air dried soil,
This has been predetermined to be 2.5% with 2,000 grams of soil and initial moisture content of 2.5% in a target moisture content of 15% it can be determined that I need to add 250 grams of water to my soil or 250 millilitres obtain the correct amount of water from the tap and pour the water into the spray bottle using the spray bottle,
Add the water to the soil and start mixing it till it becomes a uniform color and consistency when all the water is gone and the soil soil has been mixed to an even and uniform consistency it is time to place the soil in the proctor compaction mold,
Start by placing the collar back on the proctor mould spoon enough soil into the mould that when compacted the soil mould will be filled approximately one-third of the height of the mould,
Now you want to place the mould on a hard surface such as a concrete floor and compact with the Proctor hammer compact the soil using the standard Proctor hammer use 25 blows spaced evenly throughout the layer for proper compaction,
After 25 blows take the mould back to the table scarify the surface and add more soil for the next lift scarify the surface of the first compacted layer with a spoon this will ensure that the second layer will bind to the first layer,
Well spoon enough soil into the mould so that when compacted approximately 2/3 of the height of the mould will be filled again take the mould to the concrete floor and compact it with the standard Proctor hammer,
The soil should fill the mould and extend past the top of the mould an eighth inch using the straight edge trim smooth the top of the soil mould using the leftover material fill any voids that might appear in the surface of the soil,
Remove all this loose soil around the mould and way the mould without the collar loosen the soil mould from the base with two hands carry the soil in the mould into the extractor and extract the soil from the mould,
Insert the soil and mold into the extruder with two hands carefully pick up the soil specimen and carried it into the other room,
After the sample has been extruded split the sample with your knife take samples from the top and the bottom and place them in the moisture cans,
For moisture content determination weigh the cans on the scale and record the weights place the cans in the oven in 24 hours ,remove the cans and record the dry weights the dry unit weight of the compacted soil specimen,
And the moisture content can be calculated from several iterations of this test a plot of the dry unit weight vs. moisture content can be determined from this plot the maximum dry unit weight and corresponding optimum moisture content can be determined .
You must read The consistency test of cement click here
click here for other govt jobs